Check the status of the RDP protocol
Check the status of the RDP protocol on a local computer
To check and change the status of the RDP protocol on a local computer, see How to enable Remote Desktop.
Check the status of the RDP protocol on a remote computer
Important
Follow this section's instructions carefully. Serious problems can occur if the registry is modified incorrectly. Before you starty modifying the registry, back up the registry so you can restore it in case something goes wrong.
To check and change the status of the RDP protocol on a remote computer, use a network registry connection:
- First, go to the Start menu, then select Run. In the text box that appears, enter regedt32.
- In the Registry Editor, select File, then select Connect Network Registry.
- In the Select Computer dialog box, enter the name of the remote computer, select Check Names, and then select OK.
- Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server.
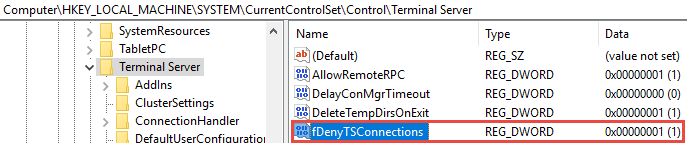
- If the value of the fDenyTSConnections key is 0, then RDP is enabled.
- If the value of the fDenyTSConnections key is 1, then RDP is disabled.
- To enable RDP, change the value of fDenyTSConnections from 1 to 0.
Check whether a Group Policy Object (GPO) is blocking RDP on a local computer
If you can't turn on RDP in the user interface or the value of fDenyTSConnections reverts to 1 after you've changed it, a GPO may be overriding the computer-level settings.
To check the group policy configuration on a local computer, open a Command Prompt window as an administrator, and enter the following command:
gpresult /H c:\gpresult.html
After this command finishes, open gpresult.html. In Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Remote Desktop Services\Remote Desktop Session Host\Connections, find the Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services policy.
-
If the setting for this policy is Enabled, Group Policy is not blocking RDP connections.
-
If the setting for this policy is Disabled, check Winning GPO. This is the GPO that is blocking RDP connections.


Check whether a GPO is blocking RDP on a remote computer
To check the Group Policy configuration on a remote computer, the command is almost the same as for a local computer:
gpresult /S <computer name> /H c:\gpresult-<computer name>.html
The file that this command produces (gpresult-<computer name>.html) uses the same information format as the local computer version (gpresult.html) uses.
Modifying a blocking GPO
You can modify these settings in the Group Policy Object Editor (GPE) and Group Policy Management Console (GPM). For more information about how to use Group Policy, see Advanced Group Policy Management.
To modify the blocking policy, use one of the following methods:
- In GPE, access the appropriate level of GPO (such as local or domain), and navigate to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Connections > Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services.
- Set the policy to either Enabled or Not configured.
- On the affected computers, open a command prompt window as an administrator, and run the gpupdate /force command.
- In GPM, navigate to the organizational unit (OU) in which the blocking policy is applied to the affected computers and delete the policy from the OU.
Check the status of the RDP services
On both the local (client) computer and the remote (target) computer, the following services should be running:
- Remote Desktop Services (TermService)
- Remote Desktop Services UserMode Port Redirector (UmRdpService)
You can use the Services MMC snap-in to manage the services locally or remotely. You can also use PowerShell to manage the services locally or remotely (if the remote computer is configured to accept remote PowerShell cmdlets).

On either computer, if one or both services are not running, start them.
Note
If you start the Remote Desktop Services service, click Yes to automatically restart the Remote Desktop Services UserMode Port Redirector service.
Check that the RDP listener is functioning
Important
Follow this section's instructions carefully. Serious problems can occur if the registry is modified incorrectly. Before you starty modifying the registry, back up the registry so you can restore it in case something goes wrong.
Check the status of the RDP listener
For this procedure, use a PowerShell instance that has administrative permissions. For a local computer, you can also use a command prompt that has administrative permissions. However, this procedure uses PowerShell because the same cmdlets work both locally and remotely.
-
To connect to a remote computer, run the following cmdlet:
PowerShellCopyEnter-PSSession -ComputerName <computer name> -
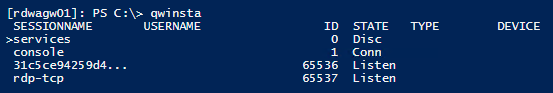
Enter qwinsta.
-
If the list includes rdp-tcp with a status of Listen, the RDP listener is working. Proceed to Check the RDP listener port. Otherwise, continue at step 4.
-
Export the RDP listener configuration from a working computer.
- Sign in to a computer that has the same operating system version as the affected computer has, and access that computer's registry (for example, by using Registry Editor).
- Navigate to the following registry entry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp - Export the entry to a .reg file. For example, in Registry Editor, right-click the entry, select Export, and then enter a filename for the exported settings.
- Copy the exported .reg file to the affected computer.
-
To import the RDP listener configuration, open a PowerShell window that has administrative permissions on the affected computer (or open the PowerShell window and connect to the affected computer remotely).
-
To back up the existing registry entry, enter the following cmdlet:
PowerShellCopycmd /c 'reg export "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-tcp" C:\Rdp-tcp-backup.reg' -
To remove the existing registry entry, enter the following cmdlets:
PowerShellCopyRemove-Item -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-tcp' -Recurse -Force -
To import the new registry entry and then restart the service, enter the following cmdlets:
PowerShellCopycmd /c 'regedit /s c:\<filename>.reg' Restart-Service TermService -ForceReplace <filename> with the name of the exported .reg file.
-
-
Test the configuration by trying the remote desktop connection again. If you still can't connect, restart the affected computer.
-
If you still can't connect, check the status of the RDP self-signed certificate.

